Zoned-In and Zoned-Out:
Changes in School Attendance Zones over Time
Magdalena Bennett
McCombs School of Business, The University of Texas at Austin
AEFP Conference
March 24th, 2023
Attendance zones, new schools, and segregation
- Schools can either attract or push away residents depending on socioeconomic characteristics (Hasan & Kumar, 2019; Gibbons, Machin, & Silva 2013; Figlio & Lucas, 2004)
Attendance zones, new schools, and segregation
Schools can either attract or push away residents depending on socioeconomic characteristics (Hasan & Kumar, 2019; Gibbons, Machin, & Silva 2013; Figlio & Lucas, 2004)
Neighborhoods have important effects on long-term outcomes (Chetty et al. 2020)
Attendance zones, new schools, and segregation
Schools can either attract or push away residents depending on socioeconomic characteristics (Hasan & Kumar, 2019; Gibbons, Machin, & Silva 2013; Figlio & Lucas, 2004)
Neighborhoods have important effects on long-term outcomes (Chetty et al. 2020)
Racial and socioeconomic disparities in the school system also have long-term effects on students (Reardon, 2016; Billings et al., 2014)
Attendance zones, new schools, and segregation
Schools can either attract or push away residents depending on socioeconomic characteristics (Hasan & Kumar, 2019; Gibbons, Machin, & Silva 2013; Figlio & Lucas, 2004)
Neighborhoods have important effects on long-term outcomes (Chetty et al. 2020)
Racial and socioeconomic disparities in the school system also have long-term effects on students (Reardon, 2016; Billings et al., 2014)
New public schools opening → Changes in attendance zones
This paper
How do changes in attendance zones (AZ) affect:
Zoned-in areas (i.e. neighborhoods)?
Zoned-out areas (i.e. neighborhoods and schools)?

This paper
How do changes in attendance zones (AZ) affect:
Zoned-in areas (i.e. neighborhoods)?
Zoned-out areas (i.e. neighborhoods and schools)?
New high schools in Texas that changed AZ → mostly gentrified areas

This paper
How do changes in attendance zones (AZ) affect:
Zoned-in areas (i.e. neighborhoods)?
Zoned-out areas (i.e. neighborhoods and schools)?
New high schools in Texas that changed AZ → mostly gentrified areas
Outcomes of interest:
Differences in scores and score gaps between race/ethnicity
Differences in school composition
Differences in neighborhood composition

What do we mean by zoned-in and zoned-out areas?
What do we mean by zoned-in and zoned-out areas?
Zoned-in area: Attendance zone for a new school S'

What do we mean by zoned-in and zoned-out areas?
Zoned-in area: Attendance zone for a new school S'

Zoned-out area: New attendance zone for school S after the opening of schools S'.
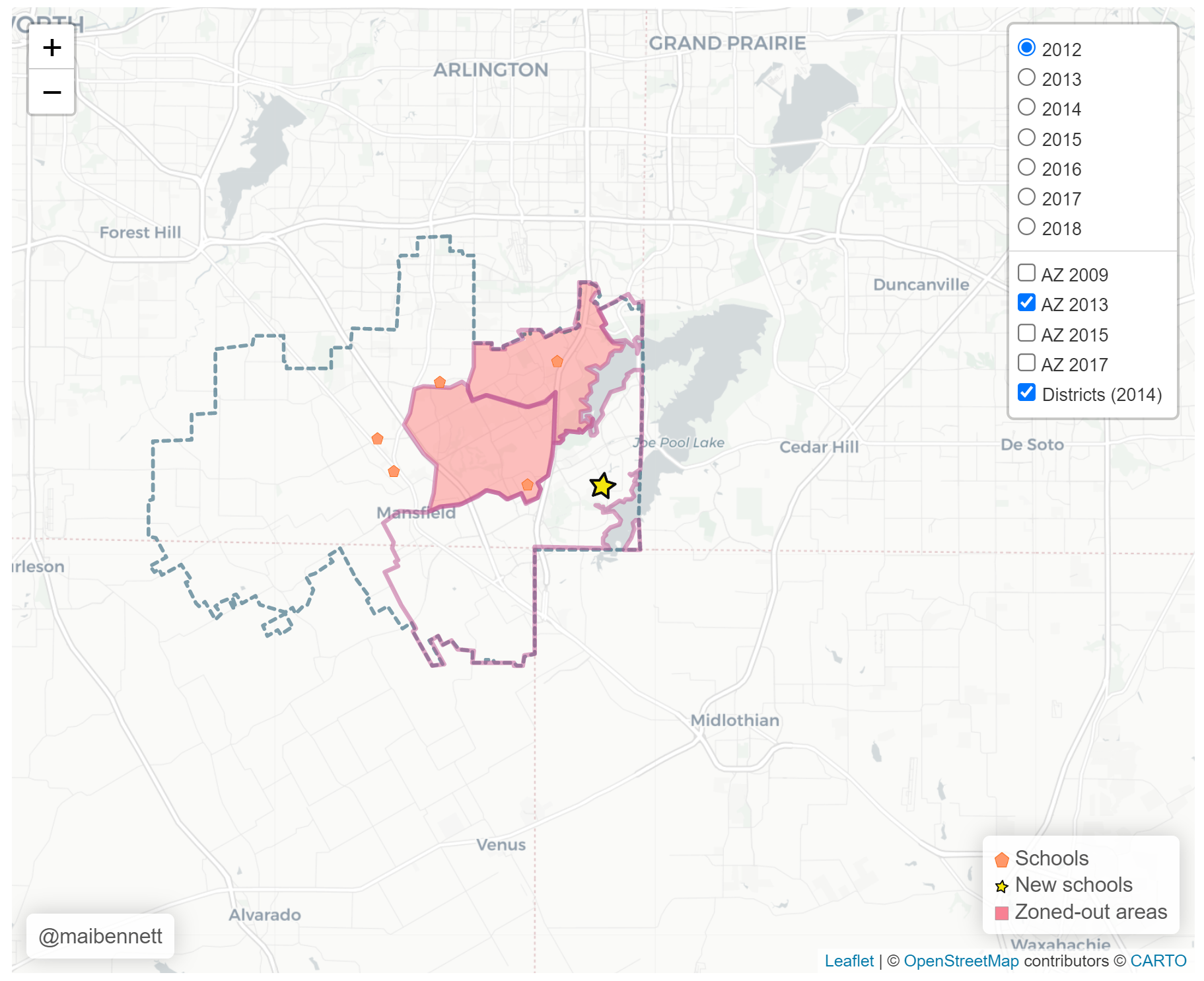
What do we mean by zoned-in and zoned-out areas?
Zoned-in area: Attendance zone for a new school S'

Spillover school: School which had a part of their catchment area zoned-in to S'.

Data
- Common Core Data (CCD) [2005-2019]: Administrative data from NCES, including demographic and socioeconomic characteristics of schools.
Data
Common Core Data (CCD) [2005-2019]: Administrative data from NCES, including demographic and socioeconomic characteristics of schools.
Texas Educacion Agency (TEA) data [2005-2019]: Performance data for schools over time.
Data
Common Core Data (CCD) [2005-2019]: Administrative data from NCES, including demographic and socioeconomic characteristics of schools.
Texas Educacion Agency (TEA) data [2005-2019]: Performance data for schools over time.
Attendance zones maps [2009-2017]: Geographic data for school boundaries over time from SABS, SABINS, and Maponics.
Data
Common Core Data (CCD) [2005-2019]: Administrative data from NCES, including demographic and socioeconomic characteristics of schools.
Texas Educacion Agency (TEA) data [2005-2019]: Performance data for schools over time.
Attendance zones maps [2009-2017]: Geographic data for school boundaries over time from SABS, SABINS, and Maponics.
Census and American Community Survey (ACS) data [2010-2019]: Demographic information at the census tract level
Data
Common Core Data (CCD) [2005-2019]: Administrative data from NCES, including demographic and socioeconomic characteristics of schools.
Texas Educacion Agency (TEA) data [2005-2019]: Performance data for schools over time.
Attendance zones maps [2009-2017]: Geographic data for school boundaries over time from SABS, SABINS, and Maponics.
Census and American Community Survey (ACS) data [2010-2019]: Demographic information at the census tract level
Housing Prices data [2005-2019]: Information about housing prices over time from CoreLogic and Zillow (coming soon).
Identification Strategy: An Augmented Synthetic Control Method
- Use a weighted average of similar districts/schools/AZ/neighborhoods to create a comparison group for affected areas.
Identification Strategy: An Augmented Synthetic Control Method
Use a weighted average of similar districts/schools/AZ/neighborhoods to create a comparison group for affected areas.
Under Augmented Synthetic Control Method (ASCM) (Ben-Michael et al., 2020) there is a correction for poor fit:
^Yaug1T(0)=∑Wi=0γiYiT+(^miT(Xi)−∑Wi=0γi^miT(Xi))
- miT: Estimator for YiT(0)
- Extrapolation for "bias correction".
- If ridge regression is used → penalization for extrapolation.
Identification Strategy: An Augmented Synthetic Control Method
Use a weighted average of similar districts/schools/AZ/neighborhoods to create a comparison group for affected areas.
Under Augmented Synthetic Control Method (ASCM) (Ben-Michael et al., 2020) there is a correction for poor fit:
^Yaug1T(0)=∑Wi=0γiYiT+(^miT(Xi)−∑Wi=0γi^miT(Xi))
- miT: Estimator for YiT(0)
- Extrapolation for "bias correction".
- If ridge regression is used → penalization for extrapolation.
Proposal of sensitivity analysis to hidden bias (Rosenbaum, 2002; Keele et al., 2019):
- How much should an unobserved confounder affect the probability of treatment (i.e. new school opening there vs in a control area) to explain away the results we find?
Broader picture: What happens to districts?
Compare districts with a new school between 2012 and 2016 vs districts with no new schools.
ASCM for different characteristics, adjusting for other baseline covariates (e.g. number of schools, enrollment, %FRPL, % race/ethnicity)

Districts with new schools increase gap in Math

... no significant change in Reading

What happens within districts?
Identify 6 new high schools between 2012-2016 that change AZ.
Compare attendance zones within districts to create a counterfactual.

What happens within districts?
Identify 6 new high schools between 2012-2016 that change AZ.
Compare attendance zones within districts to create a counterfactual.
Important caveat:
Limited sample size → under-powered.
Trends are suggestive.

Zoned-in Areas: How do neighborhoods change?
- No major changes in % white population (left) or % African American population (right)

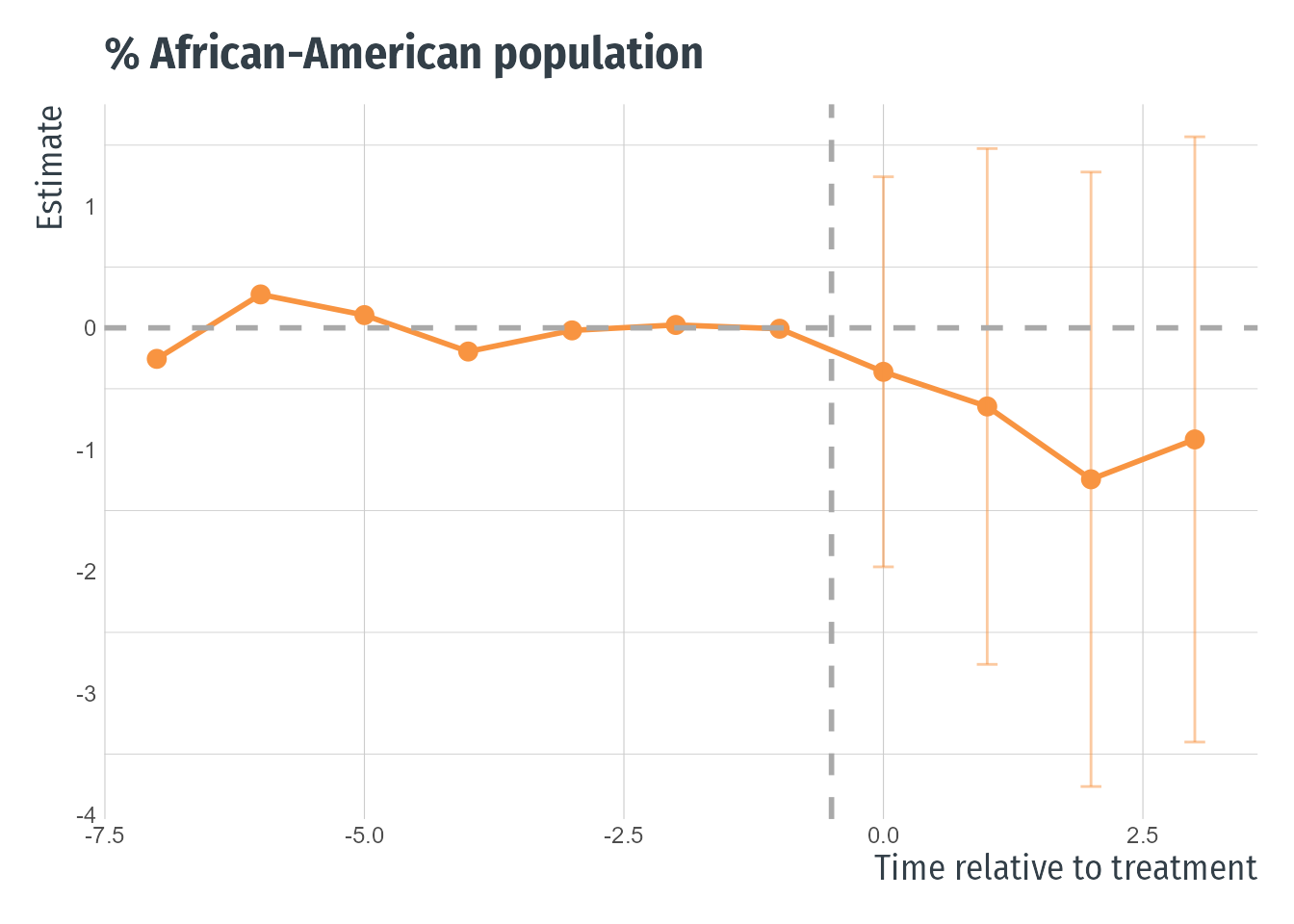
Zoned-in Areas: How do neighborhoods change?
- Suggestive increase in % of college educated population

Zoned-out Areas: How are schools affected?
- Demographics: Decreasing trend in white students enrollment (left) vs increasing trend in African American enrollment (right).


Zoned-out Areas: How are schools affected?
- Performance: Decreasing trend % of proficiency (sharper for African American students).

Zoned-out Areas: What about neighborhoods?
- Increasing trend in % of African-American population (left) and decreasing trend in % college-educated population (right).


Wrapping up
- Attendance zones have a huge role in shaping neighborhoods and nearby areas.
Wrapping up
Attendance zones have a huge role in shaping neighborhoods and nearby areas.
Importance of understanding the effects of new schools and their location and boundaries.
Wrapping up
Attendance zones have a huge role in shaping neighborhoods and nearby areas.
Importance of understanding the effects of new schools and their location and boundaries.
Effects of housing prices? Long-run outcomes?
Wrapping up
Attendance zones have a huge role in shaping neighborhoods and nearby areas.
Importance of understanding the effects of new schools and their location and boundaries.
Effects of housing prices? Long-run outcomes?
Next steps:
- Include other states (e.g. CA)
- Analyze housing prices over time.
- Heterogeneity in effect for gentrified neighborhoods?
Zoned-In and Zoned-Out:
Changes in School Attendance Zones over Time
Magdalena Bennett
McCombs School of Business, The University of Texas at Austin
AEFP Conference
March 24th, 2023